Injection Molding VS 3D Printing: Pros and Cons
Are you trying to decide between injection molding and 3D printing for your product? This article breaks down the pros and cons of each, will help you make an informed decision.
Injection molding and 3D printing are both manufacturing processes used to create products, but they differ in their approach and end results. Injection molding involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a mold to create a specific shape, while 3D printing involves building up layers of material to create a 3D object. Both processes have their own advantages and disadvantages, and are used in different industries and applications.
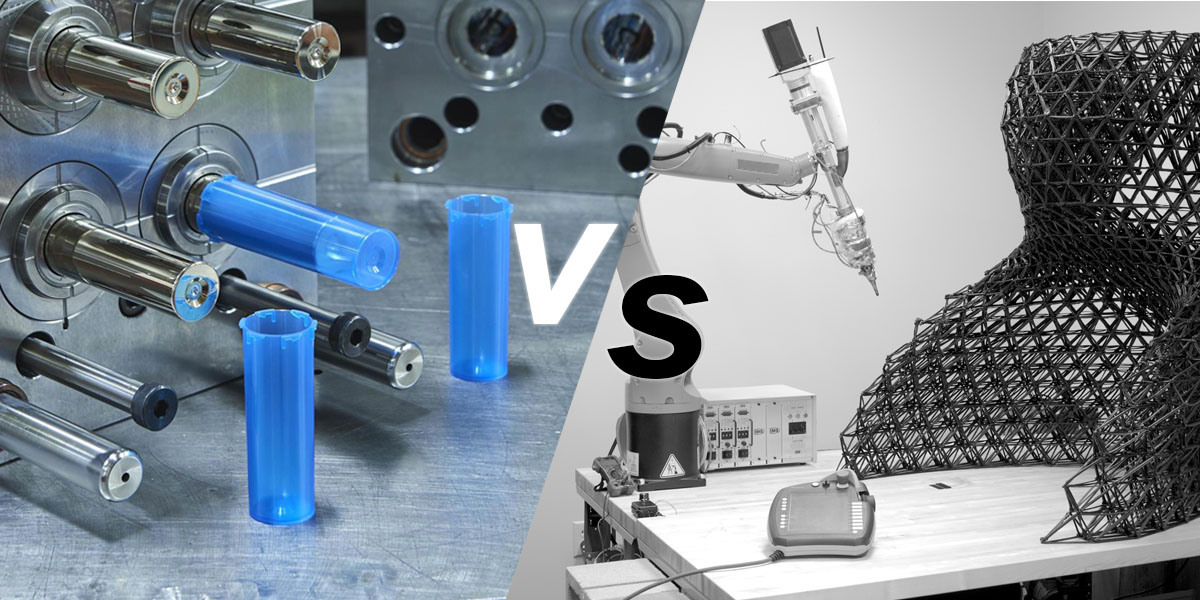
Features:
- Injection molding is a high-volume, mass production method
- 3D printing is a low-volume, customizable production method
- Injection molding can produce complex shapes with high precision
- 3D printing allows for intricate designs and customization
Benefits:
- Understanding the differences between injection molding and 3D printing can help businesses choose the best manufacturing method for their product
- Injection molding is ideal for large-scale production of standardized products, while 3D printing is better suited for small-scale production or customization
- Both methods have their own unique advantages and can be used in conjunction with each other for optimal results.
Pros and Cons
Injection molding and 3D printing are two different processes for manufacturing precision parts, with different characteristics and applications.
Processes are different:
Injection molding is by injecting molten material into a mold cavity under high pressure, allowing it to cool and solidify into the desired shape. 3D printing, on the other hand, also known as additive manufacturing, builds the desired object layer by layer from a digital design file, usually by depositing the material in a controlled manner.
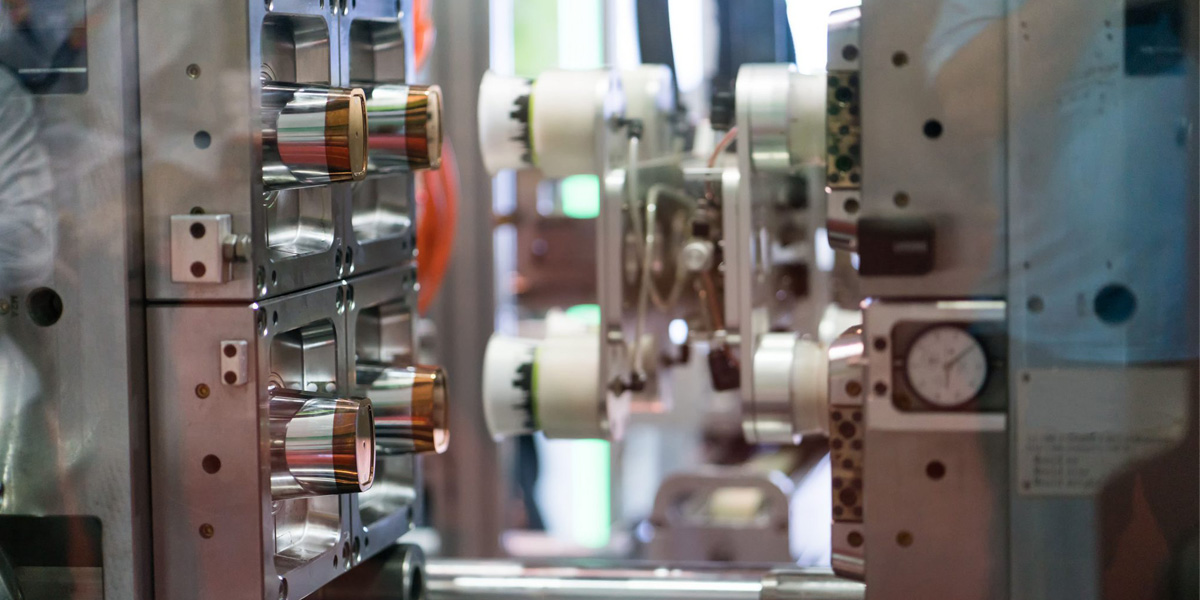
Material selection differs:
Injection molding supports a wide range of materials, including various types of plastics, metals and composites. In contrast, material options for 3D printing are expanding, but are still more limited compared to injection molding. Sometimes,advanced technologies are enabling a wider range of materials for 3D printing, with specialized options such as flexible or biocompatible materials.
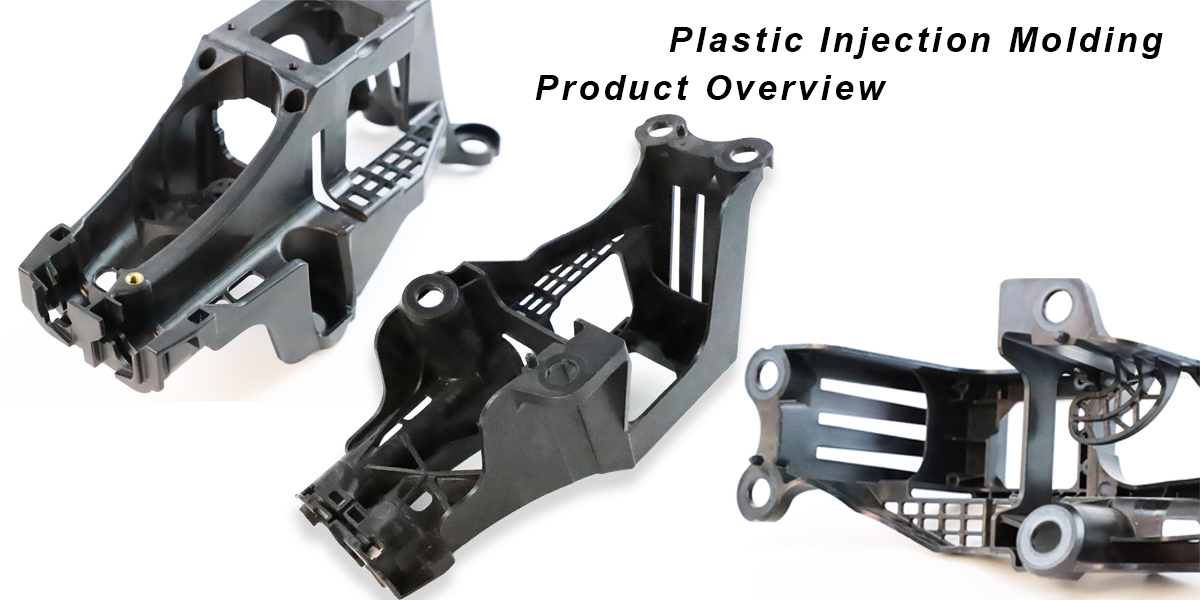

Production volumes differ:
Injection molding is well-suited for high-volume production due to the ability to quickly replicate molds and the speed of the injection process. Once the mold is ready, it can provide faster production cycles. Conversely, 3D printing is more advantageous for small production runs, prototyping and custom manufacturing because it does not require expensive molds or tooling.
Cost-effectiveness difference:
Injection molding tends to be more cost-effective for high-volume production because the cost per part decreases as the quantity increases. However, it requires a significant upfront investment to create molds, which can be relatively expensive. 3D printing, while more costly per unit compared to injection molding, is more cost effective for low volume production or one-piece parts because it does not require manufacturing molds or tooling.
Surface finishes and details differ:
Injection molding typically produces parts with smoother surface finishes and finer details than 3D printing. 3D printing can produce parts with different surface finishes, depending on the technology and setup used, but it may have a more pronounced layered appearance than injection molded parts.
Design complexity differs:
Injection molding can accommodate complex designs, but it requires consideration of mold pull angles and other production design factors in order for the finished product to be removed from the mold. 3D printing is much better at creating intricate designs and can produce parts with internal features, recesses and complex geometries more easily than injection molding, without the limitations imposed by molds.

Delivery time is different:
Because of the time required to manufacture the molds, the lead time for injection molding can be longer. However, once the mold is ready, the production cycle time for injection molding is much faster. In contrast, 3D printing typically has shorter lead times because there is no need to create a mold. When producing high volume and large parts, the process of 3D printing is relatively slow compared to injection molding.
While injection molding is suitable for high-volume production with smooth surfaces and fine details, 3D printing is advantageous for low-volume production, complex designs and rapid prototyping. The choice between the two depends on factors such as production volume, cost considerations, design complexity, and desired material properties.
If you are confused about this, you can ask GD-HUB for help.
Our professional technical team will provide the best solution for your project and give you professional advice for every doubt.